Coral: mysql create restricted user
|
MySQL Create Restricted User MySQL privileges allow each of the users to access and utilize only the areas they need to perform their tasks. This prevents a user from accidentally accessing an area where he or she should not have access this adds to the security of the MySQL server.
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
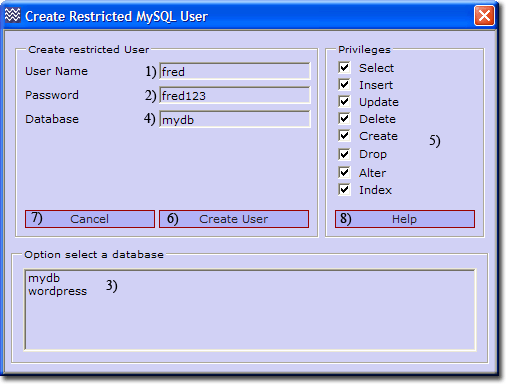
Create Restricted MySQL User using UniController
Server Configuration > MySQL > Create Restricted MySQL User
|
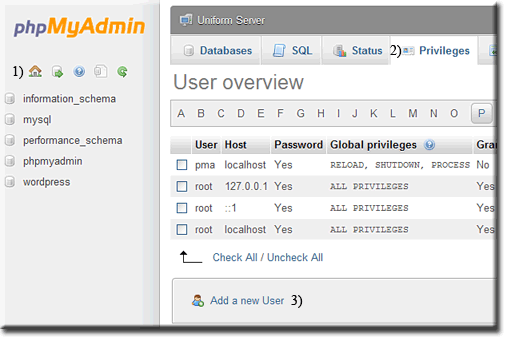
Create Restricted MySQL User using phpMyAdmin
Start UniController and start both servers, then click phpMyAmin button. To create a restricted user, proceed as follows:
Note: Assume the user to create is mike123 and password pass123. The database wordpress that the user will be assigned has aleady been created.
Open Add new user pageWhen first started the phpMyAdmin home page is displayed; you can always return to this page by clicking the home icon (1)
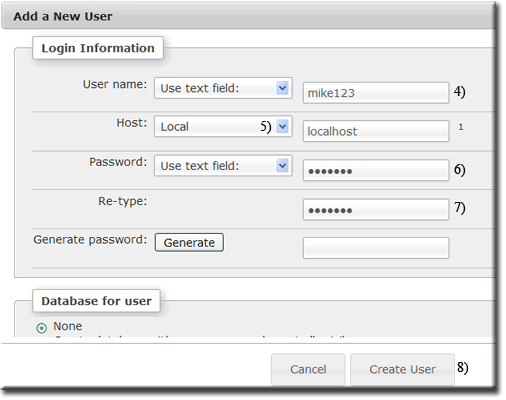
The Add a new User page is displayed. |
|
Create new userCreating a new user requires only the login information; the other fields are not required. We will assign this user to a database and set appropriate privileges as a second step. From new user page:
Note: Leave all other fields set to their defaults:
|
|
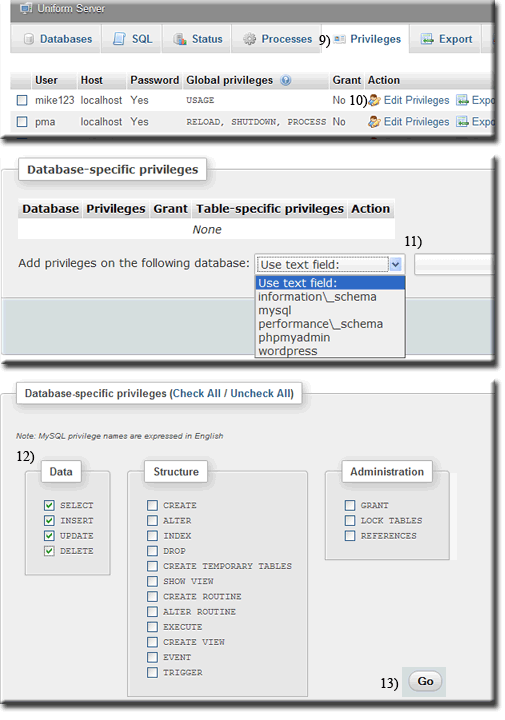
Assign user to a databaseThe new user created has now been added to the Privileges User overview page. This new entry allows a user to be assigned to a database as follows: After creating a new use you will be at the privileges page.
A new page opens displaying privileges.
This directs you to the Database-specific privileges section
|
Create Restricted MySQL User using command window
Creating a user with restricted privileges and assigning that user to an existing database can also be performed using a single SQL line.
Example user
User name to create: fred123
User password: fredpass
Existing database: wordpress
Click MySQL console, which opens a command window. Use the MySQL Client utility from here to create our example user with restricted privileges as follows:
- mysql -uroot -proot
- GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON wordpress.* TO 'fred123'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'fredpass';
- exit
The result is shown below:
C:\UniServer\usr\local\mysql\bin>mysql -uroot -proot Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 3 Server version: 5.5.14 MySQL Community Server (GPL) Copyright (c) 2000, 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql> GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON wordpress.* TO 'fred123'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'fredpass'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.09 sec) mysql> exit Bye C:\UniServer\usr\local\mysql\bin>
Note: If you have changed the MySQL root password, remember to substitute (-proot) root with your password in the above.
Delete Restricted MySQL User using command window
Delete a user (example fred123) with restricted privileges as follows:
Click MySQL console which opens a command window. Use the MySQL Client utility from here to delete our example user fred123:
|
Enter the following in a command window:
The result is shown to the right: |
C:\UniServer\usr\local\mysql\bin>mysql -uroot -proot mysql> DROP USER 'fred123'@'localhost'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec) mysql> exit Bye |
Note: If you have changed the MySQL root password, remember to substitute (-proot) root with your password in the above.
Related topics
MySQL Console
How to run a standard command window
MySQL console command window short cut