Cron Design: Cron Script Part 2: Difference between revisions
Upazixorys (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m Reverted edits by Upazixorys (Talk); changed back to last version by Ric |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Nav Cron Design}} | {{Nav Cron Design}} | ||
At the heart of Uniform Server’s portable Cron is a configuration file. This is periodically read into an array the period is defined by Cron time, which has a default setting of one minute. The array is scanned line-by-line comparing any time settings to the current time on finding a match the corresponding script is run. | At the heart of Uniform Server’s portable Cron is a configuration file. This is periodically read into an array the period is defined by Cron time, which has a default setting of one minute. The array is scanned line-by-line comparing any time settings to the current time on finding a match the corresponding script is run. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 9: | ||
Every time the script is run the configuration file is read into an array. First task of the foreach-loop is to extract a block’s option values. Each time around the loop selects a new block and extracts its option values. | Every time the script is run the configuration file is read into an array. First task of the foreach-loop is to extract a block’s option values. Each time around the loop selects a new block and extracts its option values. | ||
{| | {| | ||
|-valign= | |-valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
'''''Read Configuration file'':''' | '''''Read Configuration file'':''' | ||
| Line 18: | Line 17: | ||
| | | | ||
'''''Function Used'':''' | '''''Function Used'':''' | ||
<pre> | |||
$ini_array = parse_ini_file($file, true); | $ini_array = parse_ini_file($file, true); | ||
</pre> | |||
|-valign= | |-valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
'''''Extract Option Value'':''' | '''''Extract Option Value'':''' | ||
* Having the structure preserved means the array can be scanned with& | * Having the structure preserved means the array can be scanned with <br />a foreach loop that targets only the block title. | ||
* Hence array '''$key''' holds a block title. | * Hence array '''$key''' holds a block title. | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
<pre> | |||
foreach($ini_array as $key = | foreach($ini_array as $key => $value){ | ||
} | } | ||
</pre> | |||
|} | |} | ||
* This $key is used to target options in the bock as follows: | * This $key is used to target options in the bock as follows: | ||
| Line 40: | Line 39: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
<pre> | |||
$tim = strtotime( | $tim = strtotime("now"); //current time | ||
$tim_s = strtotime($ini_array[$key]['start']); | $tim_s = strtotime($ini_array[$key]['start']); | ||
$period = $ini_array[$key]['period']; | $period = $ini_array[$key]['period']; | ||
$path = $ini_array[$key]['path']; | $path = $ini_array[$key]['path']; | ||
$ref = $ini_array[$key]['ref']; | $ref = $ini_array[$key]['ref']; | ||
</pre> | |||
|} | |} | ||
'''''Note'':''' All times are converted to Unix timestamps. | '''''Note'':''' All times are converted to Unix timestamps. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 53: | ||
| | | | ||
'''''Configuration file example'':''' | '''''Configuration file example'':''' | ||
<pre> | |||
[dtdns] | [dtdns] | ||
| Line 80: | Line 79: | ||
ref = | ref = | ||
</pre> | |||
|} | |} | ||
'''''[[#top | Top]]''''' | '''''[[#top | Top]]''''' | ||
| Line 86: | Line 85: | ||
== Froreach logic == | == Froreach logic == | ||
{| | {| | ||
|-valign= | |-valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
'''''Description'':''' | '''''Description'':''' | ||
| Line 115: | Line 114: | ||
== Froreach logic - Alternative flow diagram== | == Froreach logic - Alternative flow diagram== | ||
{| | {| | ||
|-valign= | |-valign="top" | ||
| | | | ||
'''''Description'':''' | '''''Description'':''' | ||
| Line 124: | Line 123: | ||
'''''Code Snippet'':''' | '''''Code Snippet'':''' | ||
<pre> | |||
$ini_array = parse_ini_file($file, true); // Read cron.ini into array | $ini_array = parse_ini_file($file, true); // Read cron.ini into array | ||
foreach($ini_array as $key = | foreach($ini_array as $key => $value){ // Scan array's main keys | ||
$tim = strtotime( | $tim = strtotime("now"); //current time | ||
$tim_s = strtotime($ini_array[$key]['start']); // Start time | $tim_s = strtotime($ini_array[$key]['start']); // Start time | ||
$period = $ini_array[$key]['period']; // Period | $period = $ini_array[$key]['period']; // Period | ||
| Line 134: | Line 133: | ||
$ref = $ini_array[$key]['ref']; // Repeat time marker | $ref = $ini_array[$key]['ref']; // Repeat time marker | ||
if((float)$tim | if((float)$tim > (float)$tim_s){ // New start or started | ||
if( $ref != | if( $ref != ""){ // It was started | ||
if( (float)$tim | if( (float)$tim < (float)$ref ){ // Is it a triggered update | ||
continue; // No: Start next foreach | continue; // No: Start next foreach | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 148: | Line 147: | ||
}//if | }//if | ||
}// End foreach | }// End foreach | ||
</pre> | |||
| | | | ||
Latest revision as of 17:37, 24 November 2010
|
Cron Design: Introduction | Running Cron | Cron Script Part 1 | Cron Script Part 2 | Cron Script Part 3
|
| Uniform Server Portable Cron Design |
At the heart of Uniform Server’s portable Cron is a configuration file. This is periodically read into an array the period is defined by Cron time, which has a default setting of one minute. The array is scanned line-by-line comparing any time settings to the current time on finding a match the corresponding script is run.
This page looks at the foreach loop in detail.
Block Parameters
Before performing any foreach-loop logic processing, option values need to be extracted from the configuration file.
Every time the script is run the configuration file is read into an array. First task of the foreach-loop is to extract a block’s option values. Each time around the loop selects a new block and extracts its option values.
|
Read Configuration file:
|
Function Used: $ini_array = parse_ini_file($file, true); | ||
|
Extract Option Value:
Note: All times are converted to Unix timestamps.
|
Configuration file example: [dtdns] start = 2009-09-21 2:56:52 eriod = 600 ; 10 Mins as required by DtDNS ;path = ..\..\plugins\dtdns_updater\dtdns_updater.php ref = [db_backup] start = 2009-09-21 2:56:52 period = hourly path = ..\..\plugins\db_backup\db_backup.php ref = [moodle] start = 2009-09-21 2:56:52 period = hourly path = http://localhost/moodle/admin/cron.php ref = [drupal] start = 2009-09-21 2:56:52 period = hourly path = http://localhost/drupal/cron.php ref = |
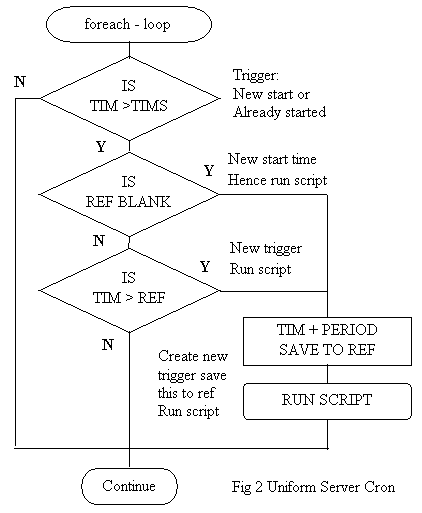
Froreach logic
|
Description: The foreach logic consists of three if statements. The first thing to note all time comparisons are relative meaning they use only the greater than or less than comparison. This caters for situations where a user moves the servers from one machine to another. Using an equal’s comparison would potential miss a time slot? Strictly speaking a start time is not necessary however it does allow staggering of intensive processes by specify a different start time for each process to be run.
|
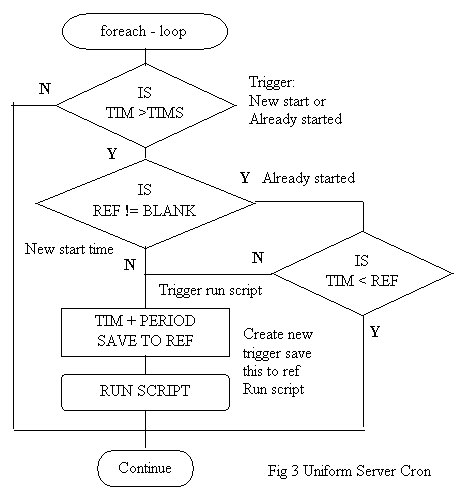
Froreach logic - Alternative flow diagram
|
Description: This flow diagram and the above are functionally identical. The above is easier to understand however if directly translated into code leads to the use of a function which is strictly not required. I prefer the flow diagram on the right although slightly more difficult to read is directly translatable into code and does not require the use of a function. Code Snippet: $ini_array = parse_ini_file($file, true); // Read cron.ini into array
foreach($ini_array as $key => $value){ // Scan array's main keys
$tim = strtotime("now"); //current time
$tim_s = strtotime($ini_array[$key]['start']); // Start time
$period = $ini_array[$key]['period']; // Period
$path = $ini_array[$key]['path']; // Path to run script
$ref = $ini_array[$key]['ref']; // Repeat time marker
if((float)$tim > (float)$tim_s){ // New start or started
if( $ref != ""){ // It was started
if( (float)$tim < (float)$ref ){ // Is it a triggered update
continue; // No: Start next foreach
}
}
//== Eiter a new start or triggered update hence run script
$ref = $tim + $period; // Create new repeat time marker
my_ini_set($file,$key,'ref',$ref); // Save to ini file for later use
// Code to Run File here
}//if
}// End foreach
|
Summary
That completes all main design areas for portable Cron.
Main point’s script uses relative comparisons so as not to miss a time event. All time references use a Unix timestamp.
Final script is shown on the next page.